Gobrs-Async 是一款功能强大、配置灵活、带有全链路异常回调、内存优化、异常状态管理于一身的高性能多线程并发编程和动态编排框架。为企业提供在复杂应用场景下动态任务编排的能力。 针对于复杂场景下,异步线程复杂性、任务依赖性、异常状态难控制性; Gobrs-Async 为此而生。
在开发复杂中台业务过程中,难免会遇到调用各种中台业务数据, 而且会出现复杂的中台数据依赖关系,在这种情况下。代码的复杂程度就会增加。 如下图所示:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.memorydoc</groupId>
<artifactId>gobrs-async-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.9-RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
克隆 Gobrs-Async 源代码
启动 Gobrs-Async-Example 模块下 GobrsAsyncExampleApplication 应用类
通过接口修改线程池中的配置。HTTP GET 路径:http://localhost:8888/gobrs/testGobrs,查看Idea 控制台 打印结果如下:
EService Begin
AService Begin
AService Finish
BService Begin
BService Finish
FService Begin
EService Finish
CService Begin
CService Finish
FService Finish
GService Begin
GService Finish
HService Begin
HService Finish
2022-11-27 19:08:51.080 INFO 61949 --- [nio-8888-exec-1] com.gobrs.async.core.TaskLoader : 【ProcessTrace】Total cost: 2536ms | traceId = 11702850586978176 | 【task】AService cost :302ms【state】:success; ->【task】BService cost :0ms【state】:success; ->【task】EService cost :602ms【state】:success; ->【task】CService cost :305ms【state】:success; ->【task】FService cost :2006ms【state】:success; ->【task】GService cost :105ms【state】:success; ->【task】HService cost :102ms【state】:success;
2551
从日志中可以看出整个流程的执行过程
【ProcessTrace】Total cost: 2536ms | traceId = 11702850586978176 | 【task】AService cost :302ms【state】:success; ->【task】BService cost :0ms【state】:success; ->【task】EService cost :602ms【state】:success; ->【task】CService cost :305ms【state】:success; ->【task】FService cost :2006ms【state】:success; ->【task】GService cost :105ms【state】:success; ->【task】HService cost :102ms【state】:success;
server:
port: 8888 # 端口: 8888
gobrs:
async:
config:
rules:
# 规则 是数组类型的 多组规则
- name: "general"
content: "AService->BService->FService->GService->HService;EService->CService;AService"
task-interrupt: false # 局部异常是否打断主流程 默认false
transaction: false
server:
port: 8888 # 端口: 8080
gobrs:
async:
enable: false # 关闭编排引擎
rules:
# 支持多命名空间
- name: "ruleName" # 规则名称
content: "AService->BService,CService,FService; BService->FService,GService;"
- name: "azh"
content: "AService->BService,CService,FService; BService->FService,GService;"
task-interrupt: false #局部异常是否打断主流程
gobrs:
async:
config:
rules:
# 规则 是数组类型的 多组规则
- name: "general"
content: "AService->BService->FService->GService->HService;EService->CService;AService"
task-interrupt: true # 局部异常是否打断主流程 默认false
transaction: true
- name: "anyConditionGeneral"
content: "AServiceCondition,BServiceCondition,CServiceCondition->DServiceCondition"
logConfig:
costLogabled: false # 开启任务耗时打印 log日志级别需要为 error 默认true
errLogabled: true # 开启任务异常打印 默认true
# AServiceCondition 、BServiceCondition、CServiceCondition任务谁返回true 谁有资格继续往下执行
- name: "anyConditionRule"
content: "AServiceCondition,BServiceCondition,CServiceCondition->DServiceCondition:anyCondition"
- name: "anyConditionRuleAppend"
content: "AServiceCondition,BServiceCondition,CServiceCondition->DServiceCondition:anyCondition->EServiceCondition"
# 官方场景一 https://async.sizegang.cn/pages/2f844b/#%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E4%B8%80
- name: "caseOne"
content: "caseOneTaskA->caseOneTaskB,caseOneTaskC,caseOneTaskD"
# 官方场景二 https://async.sizegang.cn/pages/2f844b/#%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E4%BA%8C
- name: "caseTwo"
content: "caseTwoTaskA->caseTwoTaskB->caseTwoTaskC,caseTwoTaskD"
# 官方场景三 https://async.sizegang.cn/pages/2f844b/#%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E4%B8%89
- name: "caseThree"
content: "caseThreeTaskA->caseThreeTaskB,caseThreeTaskC,caseFourTaskD->caseThreeTaskG;
caseThreeTaskA->caseThreeTaskE,caseThreeTaskF->caseThreeTaskG;"
# 官方场景四 https://async.sizegang.cn/pages/2f844b/#%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E5%9B%9B
- name: "caseFour"
content: "caseFourTaskA->caseFourTaskB->caseFourTaskC,caseFourTaskD,caseFourTaskE;
caseFourTaskA->caseFourTaskH->caseFourTaskI,caseFourTaskJ,caseFourTaskK;"
logConfig:
costLogabled: false # 关闭耗时任务打印
# 官方场景五 https://async.sizegang.cn/pages/2f844b/#%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF%E4%BA%94
- name: "caseFive"
content: "caseFourTaskA,caseFourTaskB,caseFourTaskC->caseFourTaskD:any:exclusive" # any 任意一个任务(A、B、C)执行完成后 则执行D任务
# exclusive 避免任务执行浪费 所以 D执行完成之后 会主动 中断 未完成的任务
server:
port: 9999 # 端口: 8080
如果开发者配置较多 与 springboot 配置文件放在一起有点冗余的话,可以在 resources/config 目录下创建以下配置文件都是支持的。
gobrs.yaml
gobrs.yml
gobrs.properties
规则对象又两部分组成:
规则名称(name) 约定规则的唯一标识符: 在任务触发器开发触发任务的时候需要传递。
规则内容(content) 则是规则引擎解析的核心内容,根据任务执行流程不同,任务规则配置也会不同,但是不会很复杂,详细配置流程分为一下几种场景。
:::tip 小提示 我们先说几种场景, 看完之后配置规则你自己就有感觉了
注: 下方配置中的 A、B、C 是指 动态任务在Spring中的Bean名称, 可以使用 @Task("xxx") 定义
ruleName1 代表规则名称,
:::
在流程配置task-interrupt时,有些开发者不希望任务执行的异常被gobrs-async包装。 而是想亲自进行异常捕获,根据异常类型进行不同业务处理。此时可以配置
异常抛出配置: catchable
- name: "stopAsyncRule"
content: "stopAsyncTaskA,stopAsyncTaskB,stopAsyncTaskC;stopAsyncTaskD->stopAsyncTaskE->stopAsyncTaskF"
catchable: true
如图1-1
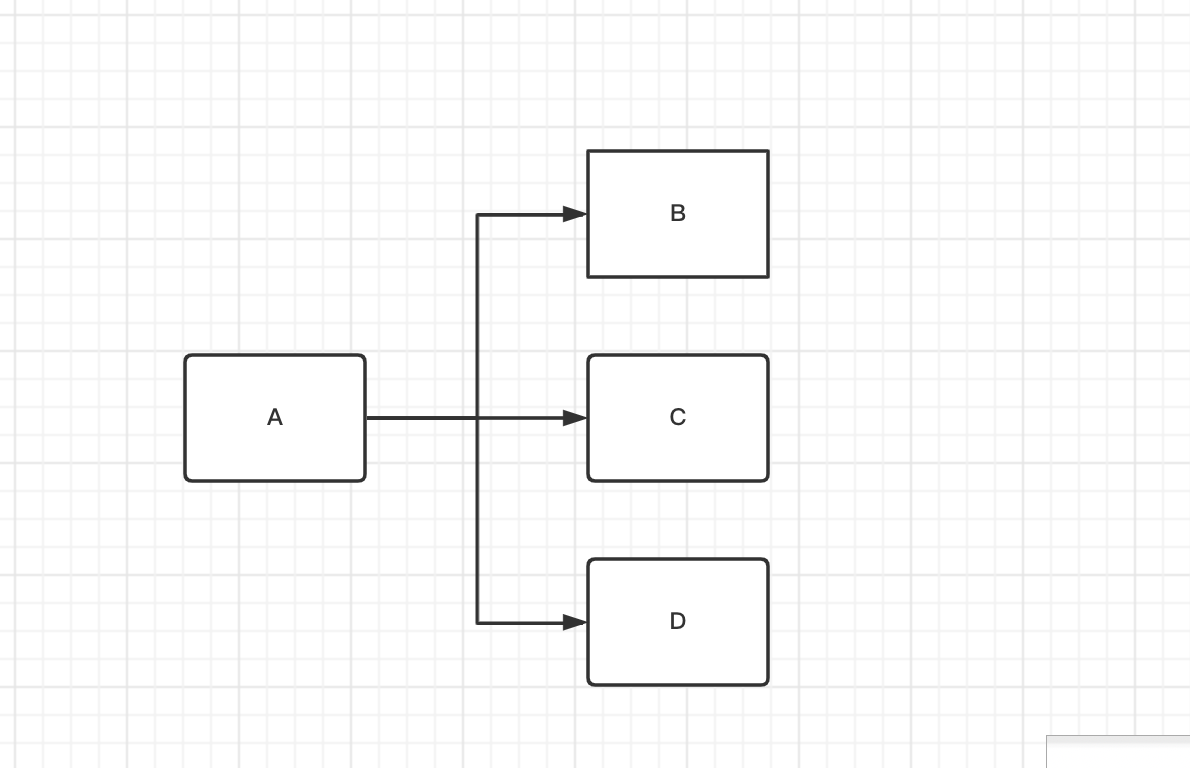
说明 任务A 执行完了之后,继续执行 B、C、D
配置
gobrs:
async:
rules:
- name: "ruleName1"
content: "A->B,C,D"
如图1-2
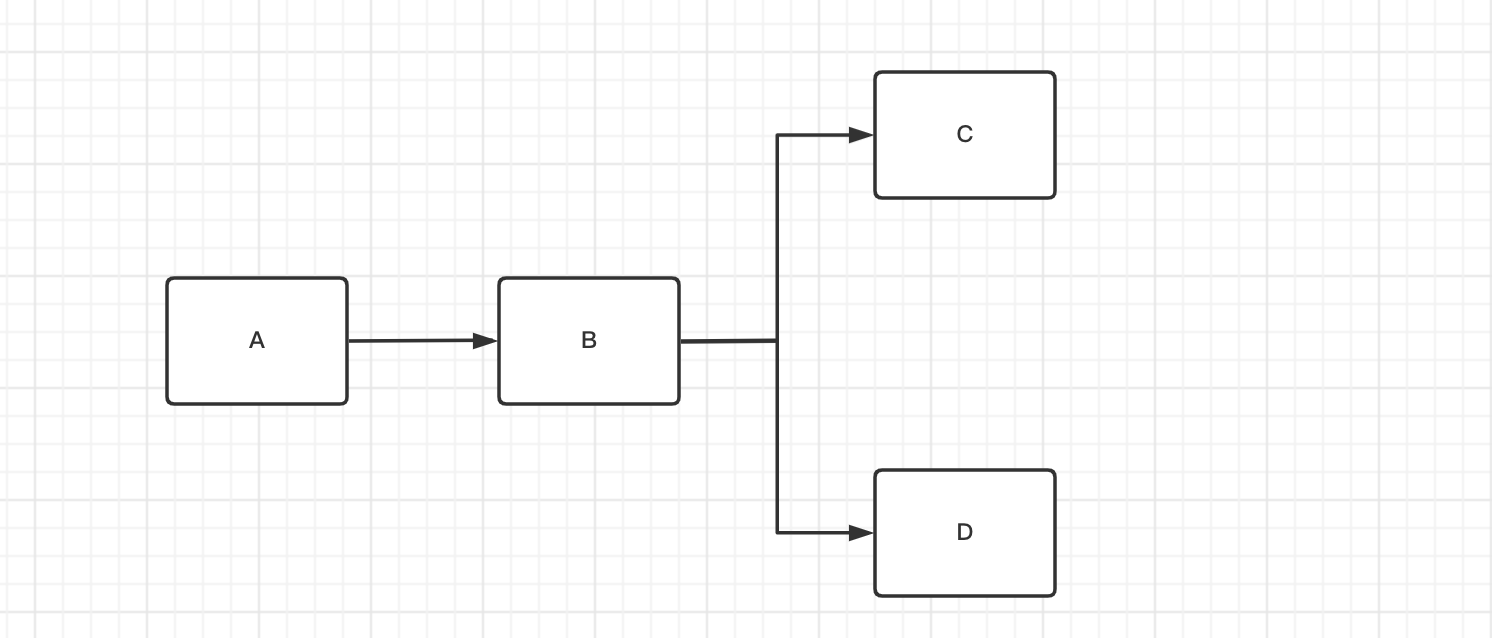
说明 任务A 执行完了之后执行B 然后再执行 C、D
配置
gobrs:
async:
rules:
- name: "ruleName1"
content: "A->B->C,D"
如图1-3
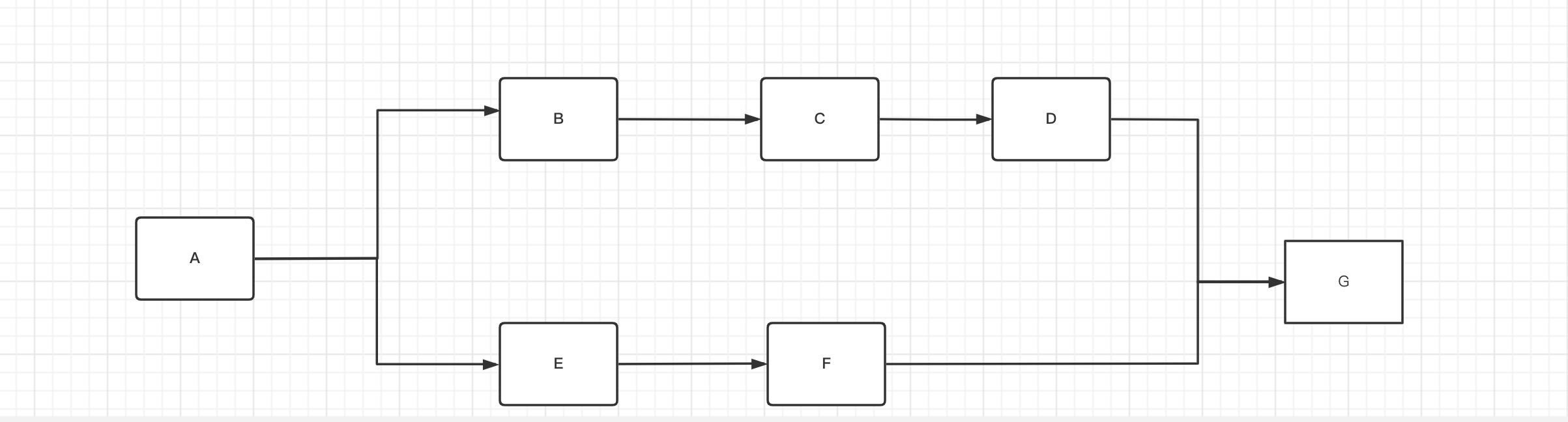
说明 任务A 执行完了之后执行B、E 然后按照顺序 B的流程走C、D、G。 E的流程走F、G
配置
gobrs:
async:
rules:
- name: "ruleName1"
content: "A->B->C->D->G;A->E->F->G"
如图1-4
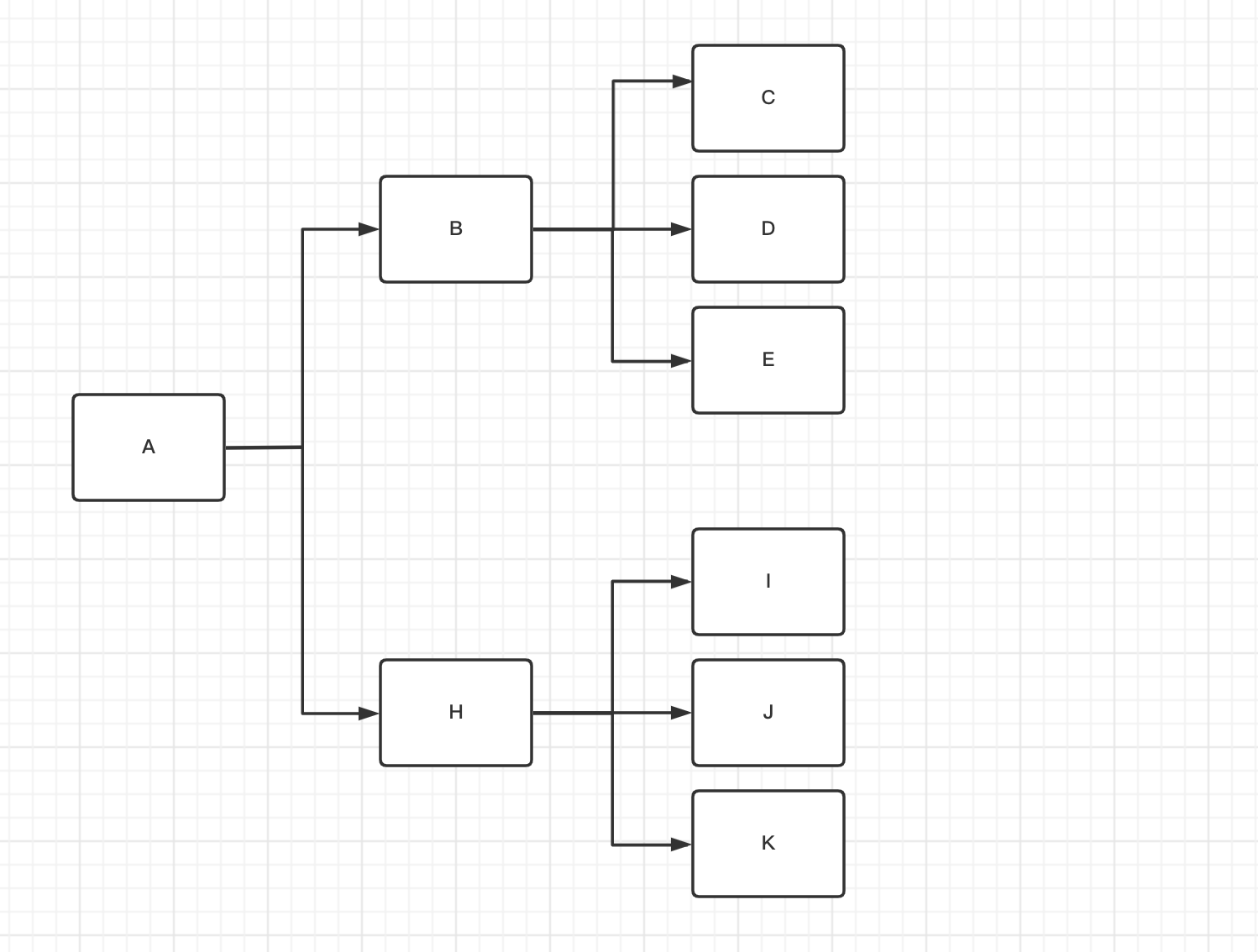
说明 这种任务流程 Gobrs-Async 也能轻松支持
配置
gobrs:
async:
rules:
- name: "ruleName1"
content: "A->B->C,D,E;A->H->I,J,K"
如图1-5
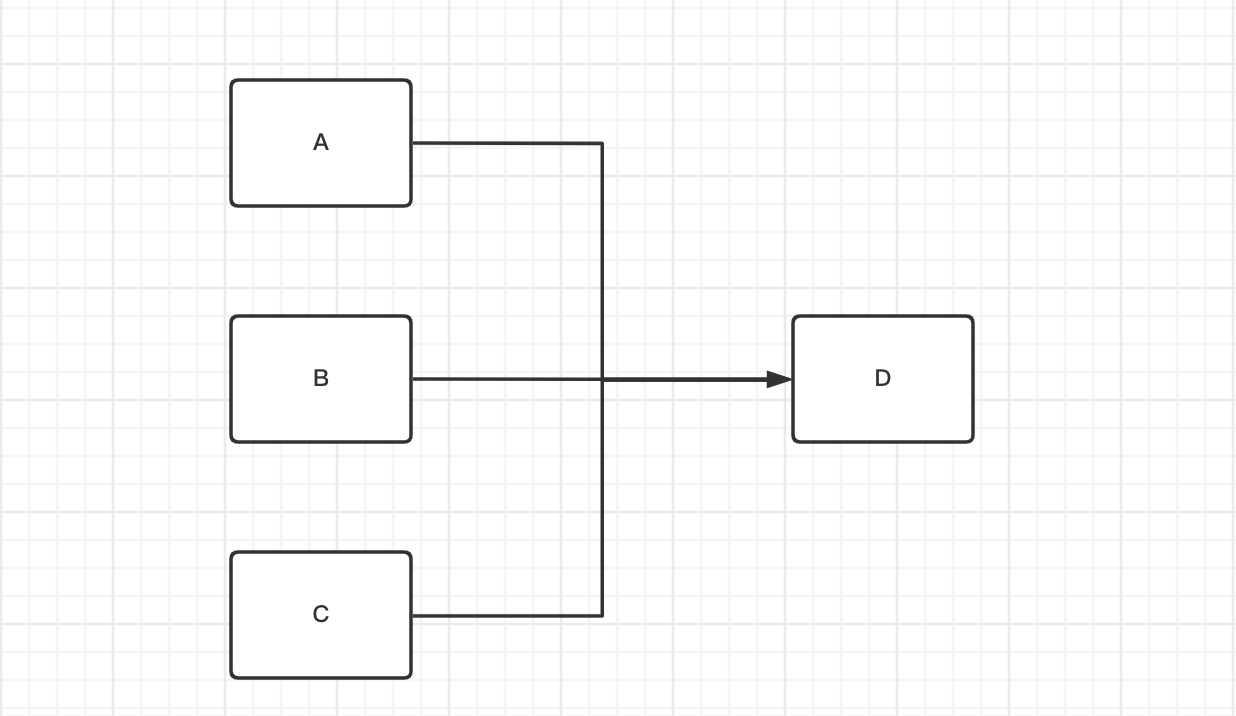
说明 A、B、C 执行完之后再执行D
配置
gobrs:
async:
rules:
- name: "ruleName1"
content: "A,B,C->D"
说明
A、B、C 任务任意一个执行完成,则立即执行任务D( 谁最快执行谁执行, 类似于任务流程竞争关系 )
此时可以使用 配置关键字 :any
配置
gobrs:
async:
## :any 是关键字 表示任意 依赖的任务执行完成立即执行自己
rules:
- name: "ruleName1"
content: "A,B,C->D:any"
说明
A、B、C 任务任意一个执行完成,则立即执行任务D( 谁最快执行谁执行, 类似于任务流程竞争关系 )
与示例不同的是, 如果 D拿到执行权后,会将自身所依赖的未完成的任务 强制中断执行(避免浪费资源,业务运行等)
此时可以使用 配置关键字 :exclusive
配置
gobrs:
async:
## :exclusive 是关键字
rules:
- name: "ruleName1"
content: "A,B,C->D:any:exclusive"
同示例二有点类似,在示例二的场景下,无法根据某一个任务的执行成功或者失败进行后续任务的处理,示例二完全根据线程调度执行的随机顺序进行执行,即谁先执行完
谁有资格继续往下执行,所以如果想 执行结果的条件 即: task 方法返回 true 则立即执行,返回false则不执行的判断条件进行控制。那么就有以下的实现方式。
(如果不清楚如何开发一个动态任务,请阅读下一章节:动态任务)
@Override
public Boolean task(Object o, TaskSupport support) {
try {
System.out.println("AServiceCondition Begin");
Thread.sleep(300);
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < i; i1++) {
i1 += i1;
}
System.out.println("AServiceCondition Finish");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// log 打印
//e.printStackTrace();
// 返回false 则没有资格执行子任务的逻辑
return false;
}
// 返回true 进行执行子任务的逻辑
return true;
}
gobrs:
async:
## :any 是关键字 表示任意 依赖的任务执行完成立即执行自己
rules:
- name: "ruleName1"
content: "A,B,C->D:anyCondition"
示例三 需要和 示例二配合生效, 因为这两种示例是结合的一种场景。
规则配置跟流程图几乎非常相近。
, 区分不同任务。-> 区分任务流。; 进行结束配置。:::tip
如果你不习惯使用以上配置符号,想自定义在配置符号, 在 Gobrs-Async 中也是支持配置的,可以根据用户使用喜欢进行灵活配置
只需要 在application.yml 中配置即可
:::
::: warning 小提示
看到这里,小伙伴们是不是已经迫不及待的想真正的体验一下 Gobrs-Async 是怎样开发一个异步任务的。 那么下面由我带领大家来感受一下 一个完整的
AsyncTask 需要怎么开发。
:::
如果你想对 任务进行全局拦截 此时就需要对每一个任务加一个特殊的标识,这样在做全局拦截的时候,就可以区分不同的任务,从而执行不同的逻辑。或者进行不同的日志打印
MQ、链路监控等等。 那么 Gobrs-Async 为你提供了支持。 只需要在 任务 Bean 中加上注解, 则会告知框架此 任务的名称
即 全局任务拦截 ,其中 注解中的 name 值对应的就是全局拦截器中参数中的 taskName
@Task(name = "itemTask")
这里 AsyncTask<T, V> 是一个泛型接口
如下:
/**
* @program: gobrs-async
* @ClassName TaskBean
* @description: 异步任务 任务参数 Object类型 ; 任务返回 Object类型
**/
@Task
public class BService extends AsyncTask<Object, Object> {
@Override
public void prepare(Object o) {
// 任务开始之前的操作 即task 之前
}
@Override
public Object task(Object o, TaskSupport support) {
String result = getResult(support, AService.class);
System.out.println("拿到的结果" + result);
System.out.println("执行BService");
return null;
}
// 什么条件下触发 task执行
@Override
public boolean nessary(Object o, TaskSupport support) {
return true;
}
// task执行成功回调用
@Override
public void onSuccess(TaskSupport support) {
}
// task 执行失败 回调
@Override
public void onFail(TaskSupport support) {
}
}
核心任务为使用者最为关注的功能方法,需要开发RPC、HTTP、IO 等消耗系统资源的业务逻辑。
@Override
public Object task(Object o, TaskSupport support) {
// todo 业务逻辑
return null;
}
Gobrs-Async 提供了 getResult 方法,无需用户关注如何获取到的依赖结果,只需要按照使用方式便可轻松获取所需结果值
@Override
public Object task(Object o, TaskSupport support) {
// 拿到 AService (任务bean) 返回的结果, 结果类型为String类型
String result = getResult(support, AService.class, String.class);
return null;
}
getResult 有三个参数
task 方法中的参数透穿即可Gobrs-Async 会根据 nessary 的返回结果,判断当前task 是否需要执行 如果返回true 则需要被执行,否则返之。
例如: 当参数为 cancel 时, 任务不执行。
@Override
public boolean nessary(String params, TaskSupport support) {
// 假如参数是cancel 则不执行当前任务
if("cancel".equals(params)){
return false;
}
return true;
}
如果你想在任务执行完成后做一些额外的操作。例如打印日志、发送邮件、发送MQ、记录信息等。 Gobrs-Async 同样也为你考虑到了。通过实现 callback 方法。会让你轻松的拿到 任务的执行结果。
@Override
public void onSuccess(TaskSupport support) {
// todo 任务成功逻辑
}
在任务异常时发送告警信息
@Override
public void onFail(TaskSupport support) {
// todo 任务执行失败回调逻辑
}
执行中的任务会出现异常的情况,如果使用者有对任务失败重试的需求,Gobrs-Async 也为你提供了支持,只需要在 需要开启重试的任务 bean
中使用 @Task(retryCount = 10) 注解,框架则自动会为你开启重试模式。 retryCount 所跟的数字为 重试次数
@Component
@Task(retryCount = 10)
public class BService extends AsyncTask<Object, Object> {
// ...
}
2022-12-09 19:36:35.444 INFO 99720 --- [pool-2-thread-1] c.g.a.test.task.retry.CaseRetryTaskA : caseRetryTaskA 使用线程---pool-2-thread-1
CaseRetryTaskA Begin
CaseRetryTaskA End
2022-12-09 19:36:35.458 INFO 99720 --- [pool-2-thread-1] c.g.a.test.task.retry.CaseRetryTaskC : caseRetryTaskC 使用线程---pool-2-thread-1
2022-12-09 19:36:35.458 INFO 99720 --- [pool-2-thread-2] c.g.a.test.task.retry.CaseRetryTaskB : caseRetryTaskB 使用线程---pool-2-thread-2
CaseRetryTaskC Begin
CaseRetryTaskB Begin
CaseRetryTaskC Finish
CaseRetryTaskB Begin
CaseRetryTaskB Begin
CaseRetryTaskB Begin
CaseRetryTaskB Begin
2022-12-09 19:36:35.475 ERROR 99720 --- [pool-2-thread-2] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : [traceId:11770907551682560] caseRetryTaskB 任务执行失败
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.gobrs.async.test.task.retry.CaseRetryTaskB.task(CaseRetryTaskB.java:27) ~[classes/:na]
at com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask.taskAdapter(AsyncTask.java:124) ~[classes/:na]
at com.gobrs.async.core.TaskActuator.call(TaskActuator.java:145) ~[classes/:na]
at com.alibaba.ttl.TtlCallable.call(TtlCallable.java:58) [transmittable-thread-local-2.11.2.jar:na]
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run$$$capture(FutureTask.java:266) [na:1.8.0_251]
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java) [na:1.8.0_251]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149) [na:1.8.0_251]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624) [na:1.8.0_251]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) [na:1.8.0_251]
2022-12-09 19:36:35.476 ERROR 99720 --- [pool-2-thread-2] c.g.a.test.inteceptor.GobrsInterceptor : Execute global interceptor error
使用者可能有这种事务需求的业务,比如 A -> B -> C 的场景,如果C执行失败了, 则通知 A和B 任务进行业务回滚。 则这种方式 Gobrs-Async 也是支持的
事务任务也需要继承 AsyncTask, 唯一的区别就是以下三个步骤。
只需要在application.yml中配置
gobrs:
async:
config:
rules:
# 规则 是数组类型的 多组规则
- name: "general"
content: "AService->BService->FService->GService->HService;EService->CService;AService"
transaction: true
在你需要进行事务的任务上进行回滚注解, Gobrs-Async 会找到 AService 任务链之前的所有任务 回调rollback 方法
@Task(callback = true)
public class AService extend AsyncTask<Object,Object>{
// ...
}
// 事务回滚 具体回滚业务需要自己实现 该方法是一个默认方法 需要自己手动重写
@Override
public void rollback(DataContext dataContext) {
//super.rollback(dataContext);
//todo rollback business
}
注意 @Task(callback = true) 需要注解在可能触发异常的任务上 官网示例
何超时任务? 顾名思义其实就是单一任务可以通过设置超时时间决定改任务是否继续执行。配置方式很简单。如下操作:
注解配置
使用 @Task注解中的 timeoutInMilliseconds 属性进行配置。
package com.gobrs.async.test.task.timeout;
import com.gobrs.async.core.TaskSupport;
import com.gobrs.async.core.anno.Task;
import com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* The type A service.
* @program: gobrs -async-starter
* @description:
* @author: sizegang
*/
@Slf4j
@Task(timeoutInMilliseconds = 300)
public class CaseTimeoutTaskA extends AsyncTask {
/**
* The .
*/
int i = 10000;
@Override
public void prepare(Object o) {
log.info(this.getName() + " 使用线程---" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public String task(Object o, TaskSupport support) {
System.out.println("CaseTimeoutTaskA Begin");
Thread.sleep(400);
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < i; i1++) {
i1 += i1;
}
System.out.println("CaseTimeoutTaskA Finish");
return "result";
}
@Override
public boolean necessary(Object o, TaskSupport support) {
return true;
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(TaskSupport support) {
}
}
所谓的监听线程池配置即:监听任务超时的线程池的核心线程数,关于为什么要配置该参数。请查看下方的原理分析。
gobrs:
async:
config:
rules:
- name: "chain1"
content: "taskA->taskB->taskC"
timeout-core-size: 200 # 核心线程数量
如果不配置则取默认值,默认值计算方式如下:
public static Integer calculateCoreNum() {
int cpuCoreNum = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
return new BigDecimal(cpuCoreNum).divide(new BigDecimal("0.2")).intValue();
}
2022-12-09 16:51:41.031 INFO 37083 --- [pool-2-thread-1] c.g.a.t.task.timeout.CaseTimeoutTaskA : caseTimeoutTaskA 使用线程---pool-2-thread-1
CaseTimeoutTaskA Begin
2022-12-09 16:51:41.355 ERROR 37083 --- [ GobrsTimer-1] com.gobrs.async.core.timer.GobrsTimer :
com.gobrs.async.core.common.exception.TimeoutException: task caseTimeoutTaskA TimeoutException
at com.gobrs.async.core.TaskLoader$1.tick(TaskLoader.java:394) ~[classes/:na]
at com.gobrs.async.core.timer.GobrsTimer.lambda$addTimerListener$0(GobrsTimer.java:80) ~[classes/:na]
at java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:511) ~[na:1.8.0_251]
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.runAndReset(FutureTask.java:308) ~[na:1.8.0_251]
at java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor$ScheduledFutureTask.access$301(ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.java:180) ~[na:1.8.0_251]
at java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor$ScheduledFutureTask.run(ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.java:294) ~[na:1.8.0_251]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149) ~[na:1.8.0_251]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624) ~[na:1.8.0_251]
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) ~[na:1.8.0_251]
2022-12-09 16:51:41.375 INFO 37083 --- [pool-2-thread-2] c.g.a.t.task.timeout.CaseTimeoutTaskB : caseTimeoutTaskB 使用线程---pool-2-thread-2
CaseTimeoutTaskB Begin
CaseTimeoutTaskB Finish
2022-12-09 16:51:41.377 INFO 37083 --- [pool-2-thread-2] c.g.a.t.task.timeout.CaseTimeoutTaskC : caseTimeoutTaskC 使用线程---pool-2-thread-2
CaseTimeoutTaskC Begin
CaseTimeoutTaskC Finish
2022-12-09 16:51:43.426 INFO 37083 --- [ main] com.gobrs.async.core.TaskLoader : 【ProcessTrace】Total cost: 2413ms【task】caseTimeoutTaskA cost :312ms【state】:fail【errMsg】: sleep interrupted; ->【task】caseTimeoutTaskB cost :0ms【state】:success; ->【task】caseTimeoutTaskC cost :2011ms【state】:success;
Hystrix 方式处理,如果对Hystrix不熟悉可以借鉴 Hystrix 熔断降级原理解析
试想下方任务流程中,在理想情况下最少用几个线程即可完成流程的执行?
taskA->taskB,TaskC->taskD->taskE,taskF 是6个线程 还是5、4、3、2 你可能已经想到了答案是 2个线程(main线程除外)即可完成该复杂的多线程流程。 为什么呢? 因为在并发执行时, TaskB、TaskC 又或者是
TaskE、TaskF 都只有两个并发的任务同时存在,所以决定使用线程数量个数的根本条件是有多少个并发任务同时执行 那么看下gobrs-async 此时有多少个线程在执行

主线程使用main
使用main
TaskA
2022-12-11 13:58:22.581 INFO 8039 --- [ main] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <11780902254572224> [taskA] execution
使用main
TaskC
使用pool-2-thread-1
TaskB
2022-12-11 13:58:22.694 INFO 8039 --- [ main] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <11780902254572224> [TaskC] execution
2022-12-11 13:58:22.694 INFO 8039 --- [pool-2-thread-1] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <11780902254572224> [taskB] execution
使用pool-2-thread-1
TaskD
2022-12-11 13:58:22.804 INFO 8039 --- [pool-2-thread-1] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <11780902254572224> [taskD] execution
使用pool-2-thread-1
使用pool-2-thread-2
TaskE
2022-12-11 13:58:22.909 INFO 8039 --- [pool-2-thread-2] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <11780902254572224> [taskE] execution
TaskF
2022-12-11 13:58:22.910 INFO 8039 --- [pool-2-thread-1] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <11780902254572224> [taskF] execution
2022-12-11 13:58:22.913 INFO 8039 --- [ main] com.gobrs.async.core.TaskLoader : 【ProcessTrace】Total cost: 440ms | traceId = 11780902254572224 | 【task】taskA cost :103ms【state】:success; ->【task】taskB cost :103ms【state】:success; ->【task】TaskC cost :103ms【state】:success; ->【task】taskD cost :106ms【state】:success; ->【task】taskE cost :101ms【state】:success; ->【task】taskF cost :101ms【state】:success;
耗时462
通过日志可以看到 TaskC使用了 TaskA的线程执行任务, 因TaskB 和 TaskC是并行的, 所以此时需要开辟新线程执行TaskB,等到TaskB执行完成后, TaskD继续使用 TaskB的 线程 pool-2-thread-1 执行任务, 此时TaskC执行完成后 发现其子任务已经被 TaskB释放后的线程拿到执行权,则不需要使用自身线程执行任务。 同理任务流程 继续往下执行。 整个流程中一共使用 3个线程(包含main线程)。
小编对比业界多种多线程并发框架,目前只有gobrs-Async 具备线程复用的能力。 具体测试用例在下方性能测试章节展示。
使用 log.error(getFormattedTraceId(), exception); 打印的日志会自动带上 traceId, getFormattedTraceId 是 AsyncTask 提供的通用方法。
@Slf4j
@Task(failSubExec = true)
public class BService extends AsyncTask {
int i = 10000;
@Override
public void prepare(Object o) {
log.info(this.getName() + " 使用线程---" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Override
public Object task(Object o, TaskSupport support) {
System.out.println("BService Begin");
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < i; i1++) {
i1 += i1;
}
try {
System.out.println(1 / 0);
} catch (Exception exception) {
log.error(getFormattedTraceId(), exception);
}
System.out.println("BService Finish");
return null;
}
}
costLogabled:打印任务流程的全链路执行过程errLogabled:开启任务异常打印 默认truegobrs:
async:
config:
rules:
- name: "optionalRule"
content: "caseOptionalTaskA->caseOptionalTaskB->caseOptionalTaskC,caseOptionalTaskD->caseOptionalTaskE->caseOptionalTaskF"
task-interrupt: false # 局部异常是否打断主流程 默认false
transaction: false
logConfig:
costLogabled: true # 开启任务耗时打印 log日志级别需要为 error 默认true
errLogabled: true # 开启任务异常打印 默认true
CaseOptionalTaskA 任务执行
CaseOptionalTaskA 任务执行完成
2022-12-11 15:47:32.511 INFO 13458 --- [o-8888-exec-152] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <11781331511388032> [caseOptionalTaskA] execution
CaseOptionalTaskB 任务执行
CaseOptionalTaskB 任务执行完成
2022-12-11 15:47:32.613 INFO 13458 --- [o-8888-exec-152] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <11781331511388032> [caseOptionalTaskB] execution
CaseOptionalTaskD 任务执行
CaseOptionalTaskD任务执行完成
2022-12-11 15:47:32.718 INFO 13458 --- [o-8888-exec-152] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <11781331511388032> [caseOptionalTaskD] execution
2022-12-11 15:47:32.718 INFO 13458 --- [o-8888-exec-152] com.gobrs.async.core.TaskLoader : 【ProcessTrace】Total cost: 311ms | traceId = 11781331511388032 | 【task】caseOptionalTaskA cost :102ms【state】:success; ->【task】caseOptionalTaskB cost :102ms【state】:success; ->【task】caseOptionalTaskD cost :105ms【state】:success;
cost 311
这里选择Tlog 日志框架, 使用方法这里就不做赘述了。感兴趣的小伙伴可以到官网查看
/**
* 启动类
*/
@SpringBootApplication
/**
* 使用gobrs-async-test 模块创建的任务 为了方便不重复创建任务了
*/
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.gobrs.async"})
public class GobrsAsyncExampleApplication {
/**
* Tlog 日志打印框架 官网: https://tlog.yomahub.com/
*/
static {
AspectLogEnhance.enhance();
}
/**
* The entry point of application.
*
* @param args the input arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GobrsAsyncExampleApplication.class, args);
}
}
集成方式请参考源码示例项目 gobrs-async-example 或者直接下载源码查看。 源码地址
在Gobrs-Async中默认规则只会加载一次,可能有朋友可能会有规则动态变化的需求,使用程序动态修改规则配置。而不需要重新启动程序。那么对于这种需求 Gobrs-Async 同样支持。
Gobrs-Async 默认使用CopyOnWrite 机制更新的规则配置,并发度更高。同时维护了线程安全机制。
// 规则热加载器
@Resource
private RuleThermalLoad ruleThermalLoad;
// 热更新规则任务 无需启动程序, 只需要将规则交给 规则热加载器 即可完成接入
public void updateRule(Rule rule) {
// 单任务修改
Rule r = new Rule();
r.setName("ruleName");
r.setContent("AService->CService->EService->GService; BService->DService->FService->HService;");
ruleThermalLoad.load(rule);
// 批量修改
List<Rule> updateRules = new ArrayList<Rule>();
updateRules.add(r);
// updateRules.add(...);
ruleThermalLoad.load(updateRules);
}
如果日志打印如下提示,说明配置热更新成功
com.gobrs.async.engine.RuleThermalLoad : rule test update success
在流程中如果你想在某种业务场景下手动关闭任务流程执行。 并在任务触发器执行完成之后,根据AsyncResult 的结果,判断不同的业务逻辑
Gobrs-Async 也为你提供了途径。 用户只需要在 异步任务的 task方法中 手动跳用 stopAsync 透传TaskSupport
无需关注内部实现,即可轻松完成关闭主流程。
stopAsync 方法有两个参数说明如下:
TaskSupport: Gobrs-Async 使用参数, 透传即可。expCode : 中断状态码,可自定义枚举
@Override
public Map task(DataContext dataContext, TaskSupport support) {
try {
// todo 执行任务
} catch (Exception e) {
// todo 根据不同的异常 处理返回不同的 中断码
if (e instanceof RedirectSimpleException) {
// 中断任务流程
stopAsync(support, PRODUCT_NOT_FOUND);
return null;
}
stopAsync(support, SYSTEM_DEMOTION);
}
return null;
}
任务触发器执行完成 执行完成之后,会获取 AsyncResult 任务流程执行结果。
根据不同的中断码,执行不同的业务逻辑。
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap();
// 任务流程名称 , 任务流程传入参数, 任务流程超时时间
AsyncResult asyncResult = gobrsAsync.go("ruleName", () -> params, timeOut);
if(asyncResult.getExpCode().equals(100)){
// 业务一
}else if(asyncResult.getExpCode().equals(200)){
// 业务二
}
在执行 A->B->C 过程中,如果A 执行异常,Gobrs-Async 默认不会继续执行 B、C任务了,但是如果使用者有特殊需求, 想要继续执行 B、C任务,
这种情况Gobrs-Async 也提供支持, 只需要在 Task注解中声明 failSubExec 即可继续执行任务流程。
默认 failSubExec=false
@Service
@Task(failSubExec = true)
public class BService extends AsyncTask<Object, Object> {
// ...
}
何为状态任务流程? 其实很好理解,比如说有 A、B、C、D 四个任务。D任务的执行依赖A、B、C三个任务, 但是A B C 的执行状态有不好确定(运行时状态)
如果想根据任务返回值的状态决定流程如何执行怎么办呢? 比如说A B C三个任务中根据不通的业务逻辑会返回不通的任务状态。遇到这种情况可以使用Gobrs-Async
为你提供的动态状态能力选择任务执行。
比如: A 业务返回true 则就执行D任务,无需关心B、C任务的执行过程。
与开发一个普通任务不通的是,返回结果需要是 AnyConditionResult 类型。
package com.gobrs.async.test.task.condition;
import com.gobrs.async.core.TaskSupport;
import com.gobrs.async.core.anno.Task;
import com.gobrs.async.core.common.domain.AnyConditionResult;
import com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* The type A service.
*
* @program: gobrs -async-starter
* @ClassName AService
* @description: 任务依赖类型
* AServiceCondition,BServiceCondition,CServiceCondition->DServiceCondition:anyCondition
* <p>
* 简化配置
* <p>
* A,B,C->D:anyCondition
* <p>
* D根据 A,B,C 返回的任务结果中的 AnyCondition 的state状态 进行判断是否继续执行 子任务。
* @author: sizegang
* @create: 2022 -03-20
*/
@Task(failSubExec = true)
public class AServiceCondition extends AsyncTask {
/**
* The .
*/
int sums = 10000;
@Override
public AnyConditionResult<String> task(Object o, TaskSupport support) {
AnyConditionResult.Builder<String> builder = AnyConditionResult.builder();
try {
System.out.println("AServiceCondition Begin");
Thread.sleep(300);
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < sums; i1++) {
i1 += i1;
}
System.out.println("AServiceCondition Finish");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 异常返回false
return builder.setState(false).build();
}
return builder.setState(true).build();
}
}
AnyConditionResult.Builder<String> builder = AnyConditionResult.builder(); 构造函数默认创建一个 true的状态。
2022-12-09 17:48:44.676 INFO 58639 --- [ main] com.gobrs.async.core.GobrsPrint : Gobrs-Async Load Successful
CServiceCondition Begin
BServiceCondition Begin
AServiceCondition Begin
BServiceCondition Finish
AServiceCondition Finish
DServiceCondition Begin
DServiceCondition Finish
2022-12-09 17:48:45.435 INFO 58639 --- [pool-1-thread-1] com.gobrs.async.core.TaskLoader : 【ProcessTrace】Total cost: 334ms | traceId = 11770483512420224 | 【task】BServiceCondition cost :3ms【state】:success; ->【task】AServiceCondition cost :305ms【state】:success; ->【task】DServiceCondition:anyCondition cost :0ms【state】:success;
377
【gobrs-async】 testCondition 执行完成
如果你想在任务流程执行过程中,某一任务执行异常,想让整个任务流程停止下来。并且可自定拦截这个异常,可在发生异常时 执行报警或者打印异常等业务。
配置application.yml
gobrs:
async:
config:
rules:
# 规则 是数组类型的 多组规则
- name: "general"
content: "AService->BService->FService->GService->HService;EService->CService;AService"
task-interrupt: true # 局部异常是否打断主流程 默认 false
实现 AsyncExceptionInterceptor 接口,开发一个自定义的异常处理拦截器
/**
* @program: gobrs-async
* @ClassName GobrsExceptionInter
* @description: 主流程中断异常自定义处理
* @author: sizegang
* @create: 2022-02-19 22:55
* @Version 1.0
**/
@Component
public class GobrsExceptionInter implements AsyncTaskExceptionInterceptor {
@Override
public CompletionException exception(Throwable throwable, Boolean state) {
System.out.println("自定义全局异常 exceptor Interceptor 触发");
return new CompletionException(throwable);
}
}
默认 Gobrs-Async 对全局拦截器开关是关闭的,如果流程中某一任务异常,只会停止所依赖该异常任务的任务停止,并调用callback 通知 下游任务
有些小伙伴可能不满足与单任务的拦截,希望有一个统一拦截的入口,而不是对每一个任务做单独的处理。那么 Gobrs-Async 也为您提供了支持。
实现 AsyncTaskPreInterceptor 接口,开发一个自定义的任务流程前置 全局拦截器。
/**
* @program: m-detail
* @ClassName AsyncTaskPreInterceptor
* @description:
* @author: sizegang
* @create: 2022-03-24
**/
@Component
public class TaskPreInterceptor implements AsyncTaskPreInterceptor<DataContext> {
/**
*
* @param params 参数
* @param taskName 任务名称
*/
@Override
public void preProcess(DataContext params, String taskName) {
}
}
实现 TaskPostInterceptor 接口,开发一个自定义的任务流程前置 全局拦截器
/**
* @program: m-detail
* @ClassName AsyncTaskPreInterceptor
* @description:
* @author: sizegang
* @create: 2022-03-24
**/
@Component
public class TaskPostInterceptor implements AsyncTaskPostInterceptor {
/**
*
* @param result 任务结果
* @param taskName 任务名称
*/
@Override
public void postProcess(Object result, String taskName) {
}
}
Gobrs-Async 默认使用的是 Executors.newCachedThreadPool() 的线程池, 如果你想自定义线程池。满足自己的线程池需求。
只需要 GobrsAsyncThreadPoolFactory 对象,如下:
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
@Autowired
private GobrsAsyncThreadPoolFactory factory;
@PostConstruct
public void gobrsThreadPoolExecutor(){
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(300, 500, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue());
factory.setThreadPoolExecutor(threadPoolExecutor);
}
开发者可能有这种苦恼,线程池在运行时是在项目初始化的时候从application.yml中 加载的, 一旦程序运行起来之后,就无法修改使用的线程池了。
如果自己公司有分布式配置中心,可以实时更新程序内存的应用的话,那么gobrs也为你提供了入口。
在我们公司是有自己的热更新组件的,所有可以如下使用:
{
corePoolSize: 210,
maxPoolSize: 600,
keepAliveTime: 30,
capacity: 10000,
threadNamePrefix: "m-detail"
rejectedExecutionHandler: "CallerRunsPolicy"
}
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
@Autowired
private GobrsAsyncThreadPoolFactory factory;
@Resource
private DUCCConfigService duccConfigService;
@PostConstruct
public void gobrsThreadPoolExecutor() {
// 从配置中心拿到 线程池配置规则 DuccConstant.GOBRS_ASYNC_THREAD_POOL 为线程池配置在配置中心的key
String config = duccConfigService.getString(DuccConstant.GOBRS_ASYNC_THREAD_POOL);
ThreadPool threadPool = JSONObject.parseObject(config, ThreadPool.class);
// 通过gobrs-async 提供的构造器进行构造线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = ThreadPoolBuilder.buildByThreadPool(threadPool);
factory.setThreadPoolExecutor(executor);
listenerDucc();
}
// 监听配置中心 线程池改动
private void listenerDucc() {
duccConfigService.addListener(new DuccListener(DuccConstant.GOBRS_ASYNC_THREAD_POOL, property -> {
log.warn("监听到DUCC配置GobrsAsync 线程池配置变更,property:{}", JSON.toJSONString(property.getValue()));
ThreadPool threadPool = JSONObject.parseObject(property.getValue().toString(), ThreadPool.class);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = ThreadPoolBuilder.buildByThreadPool(threadPool);
factory.setThreadPoolExecutor(executor);
// 线程池更新成功
log.warn("GobrsAsync thread pool update success");
}));
}
}
- name: "optionalRule"
content: "caseOptionalTaskA->caseOptionalTaskB->caseOptionalTaskC,caseOptionalTaskD->caseOptionalTaskE->caseOptionalTaskF"
如果开发者在调用时只希望执行 caseOptionalTaskD , 则在任务链中 只需要执行caseOptionalTaskA、caseOptionalTaskB、caseOptionalTaskD 三个任务即可即可。 其他任务不需要执行
,提供了随机选择流程中任务执行的能力。
gobrsAsync.go方法的第三个参数 Set<String> 需要传递 要执行的任务 bean 名称。
@Test
public void testOptional() {
Map<Class, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
Set<String> options = new HashSet<>();
options.add("caseOptionalTaskD"); # options中添加要执行的任务 bean 名称
AsyncResult asyncResult = gobrsAsync.go("optionalRule", () -> params, options, 300000);
}
CaseOptionalTaskA 任务执行
CaseOptionalTaskA 任务执行完成
2022-12-11 15:47:32.511 INFO 13458 --- [o-8888-exec-152] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <0><11781331511388032> <11781331511388032> [caseOptionalTaskA] execution
CaseOptionalTaskB 任务执行
CaseOptionalTaskB 任务执行完成
2022-12-11 15:47:32.613 INFO 13458 --- [o-8888-exec-152] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <0><11781331511388032> <11781331511388032> [caseOptionalTaskB] execution
CaseOptionalTaskD 任务执行
CaseOptionalTaskD任务执行完成
2022-12-11 15:47:32.718 INFO 13458 --- [o-8888-exec-152] com.gobrs.async.core.task.AsyncTask : <0><11781331511388032> <11781331511388032> [caseOptionalTaskD] execution
2022-12-11 15:47:32.718 INFO 13458 --- [o-8888-exec-152] com.gobrs.async.core.TaskLoader : <0><11781331511388032> 【ProcessTrace】Total cost: 311ms | traceId = 11781331511388032 | 【task】caseOptionalTaskA cost :102ms【state】:success; ->【task】caseOptionalTaskB cost :102ms【state】:success; ->【task】caseOptionalTaskD cost :105ms【state】:success;
cost 311
在做 ISV (京东商城ISV组件化建设) 建设时, 楼层中的多个组件可能存在着任务流程的编排, 所需要的上游数据数量多少不一,所以此时就需要进行编排流程中的任务选择执行处理了。
如下对每个组件进行编排数据编排处理。

skywalking 是全链路监控平台,因为skywalking 不兼容多线程traceId,所以gobrs-async 提供skywalking插件
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.memorydoc</groupId>
<artifactId>gobrs-async-skywalking-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2.9-RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
只需引入依赖即可完成与skywalking完美适配。是不是感觉很神奇!
各位开发同学已经都知道,全链路traceId是打印在日志里的方便链路追踪的序列号。 有了它你可以轻松追踪线上问题,简单好用。
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.memorydoc</groupId>
<artifactId>gobrs-async-trace-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2.9-RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
只需引入依赖即可完成与skywalking完美适配。是不是感觉很神奇!
需要在SpringBoot启动类中编写
static {
GobrsLogger.logger();
}
Gobrs-Async日志插件封装了 Tlog 如有使用问题请访问Tlog官网。
对于这个项目,是否有什么不一样看法,欢迎在 Issue 一起沟通交流; 群二维码七天会失效,可以添加作者微信进交流群
 |
 |
此处可能存在不合适展示的内容,页面不予展示。您可通过相关编辑功能自查并修改。
如您确认内容无涉及 不当用语 / 纯广告导流 / 暴力 / 低俗色情 / 侵权 / 盗版 / 虚假 / 无价值内容或违法国家有关法律法规的内容,可点击提交进行申诉,我们将尽快为您处理。
1. 开源生态
2. 协作、人、软件
3. 评估模型